3D Printing Related
Introduction
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is a family of processes that produces objects by adding material in layers that correspond to successive cross-sections of a 3D model.
Plastics and metal alloys are the most commonly used materials for 3D printing, but it can work on nearly anything—from concrete to living tissue.
(Source: Anycubic)
Environment and Software
- Computer
- 3D Printer
- 3D Software
- Consumables
- Additional materials
PART 1
Types of 3D printing Tech
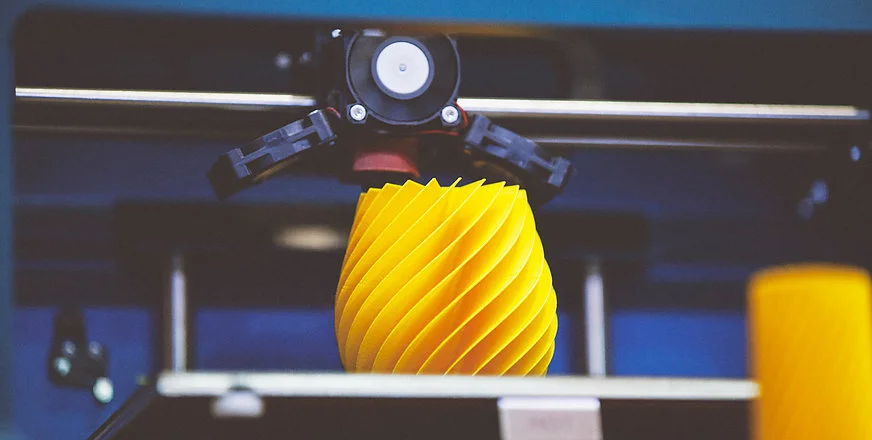
FDM: Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Material Deposition
- Can print very large
- Has over 50 different materials like ABS, ASA, PC, PPSF, and ULTEM
- Many color options
- Does sweat the small details, has noticeable layer stepping
- Great for large custom fixtures
(Photo Source: Amfg.ai)
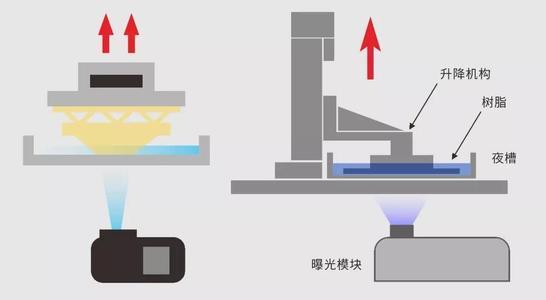
SLA: Stereolithography(SLA),Vat Photopolymerization
- Engineered resins to “act like” plastics
- High variety of materials
- Best surface smoothness from direct print
- Best detail resolution
- Tolerances: XY plane: +/- 0.005” for the first inch, plus +/- 0.002” for every inch thereafter. Z plane: +/- 0.010” for the first inch, plus +/- 0.002” for every inch thereafter.
- Typically used in prototyping phase
- Certain taste and toxicity
(Photo Source: Autodesk)
DLP:
High curing rate (high optical efficiency at 405nm)
low cost
High resolution
High reliability
Long service life
(Photo Source: zhimg)
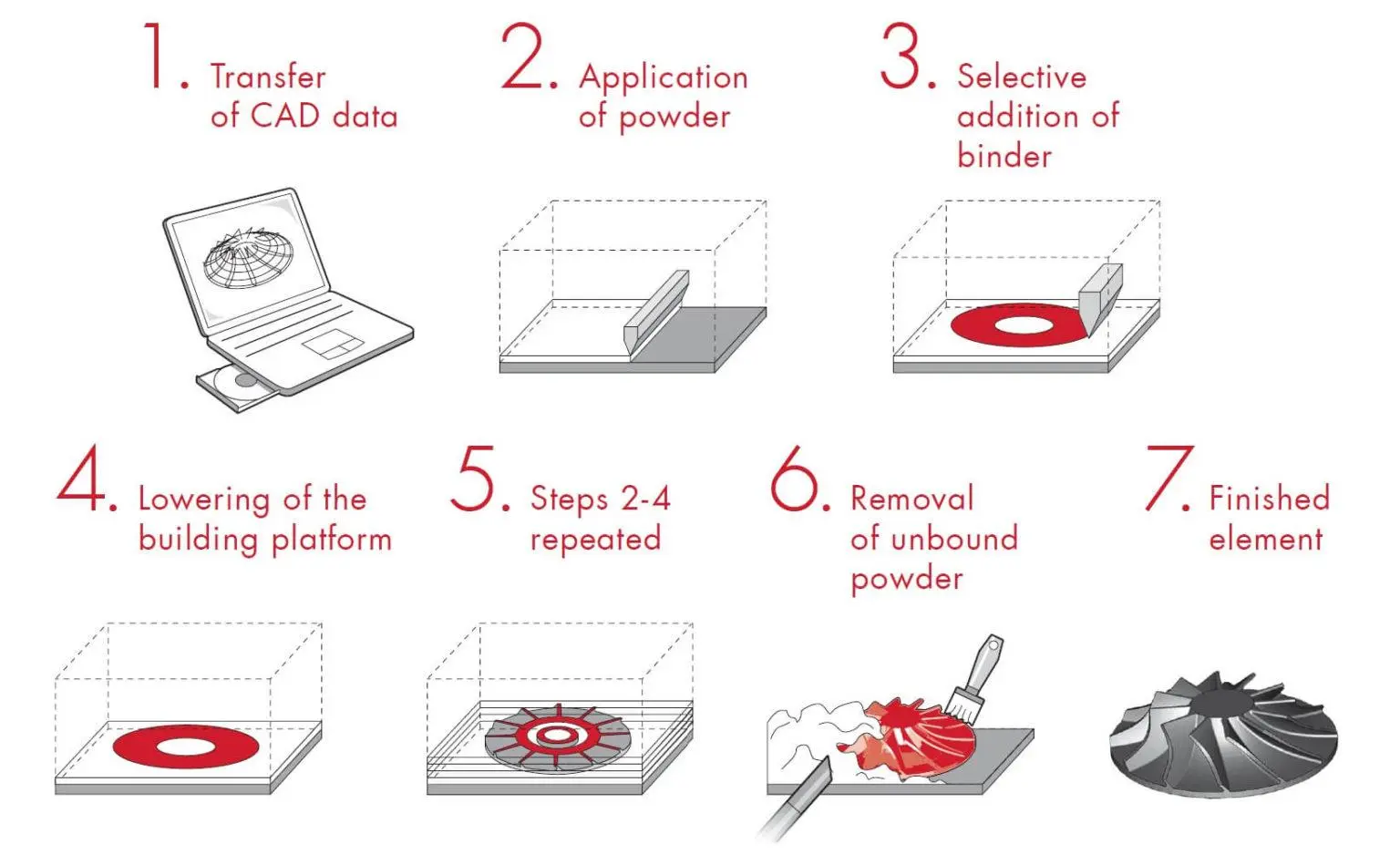
3DP: Three Dimensional Printing and Gluing(3DP), Binder Jetting, Inkjet Powder Printing
- 3DP process is similar to SLS process
- Formed with powder materials
- ceramic powder, metal powder
(Photo Source: Engineeringproductdesign)
SLS: Selective Laser Sintering(SLS) Successfully developed by C.R. dechard of the University of Texas at Austin in 1989.
Known for high complexity in parts
Uses nylon as a durable, flexible, and chemical resistant
material
Water-tight
Tolerance of +/- 0.005′′ or +/- 0.002′′ per inch, whichever is greater
Lower diversity in material/finishing options, has a textured or grainy surface
Often chosen for internal components/non-cosmetic parts (jigs, fixtures)
Photo
(Photo Source: Engineeringproductdesign)
MJF:HP Multi Jet Fusion(MJF)
Known for high complexity in parts
Slightly higher throughput than SLS
Uses nylon as a durable, flexible, and chemical resistant material
Water-tight
Tolerance of +/- 0.012′′ or +/- 0.002′′ per inch, whichever
is greater
Lower diversity in material/finishing options, has a textured or grainy surface
Some resource links:
PART 2
Full Process
STEP 1
Download and Install 3D design Software(in 21 Century)
Some Examples:
STEP 2
Download and Install Slicing software (in 21 Century)
STEP 3
Prepare or make a 3D model and export it as an STL file
How to export it as an STL file?
If you use Fusion 360 please click Here
If you use AutoCAD please clickHere
If you use Blender please clickHere
STEP 4
Import the .stl file to Slicing software
If you use Cura please click Here
If you use Chitubox please click Here
STEP 5
Add supports to objects and slicing in software
If you use Cura please click Here
If you use Chitubox please click Here
STEP 5
Buy an 3D printer and assembly equipment:stuck_out_tongue_winking_eye:
STEP 6
Check the file formats supported by your 3D printer and export them.
If you use Cura please click Here
If you use Chitubox please click Here
STEP 6
Do the preparatory work and let your printer start working
If you use the FDM 3D Printer, make sure you follow the printer’s instructions.
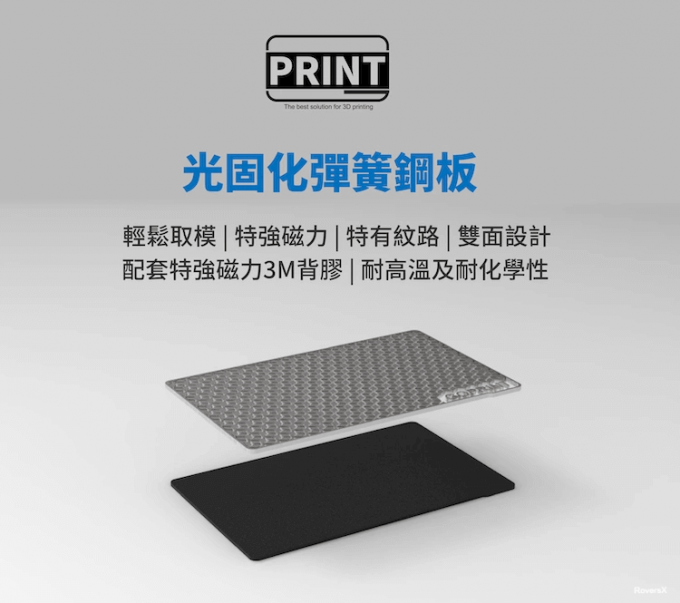
If you use the SLA 3D Printer, make sure you follow the printer’s instructions. I suggest you add SLA spring magnet plates and use the Water-Washable Resins(If you don’t want to use pungent amounts of alcohol). At the same time, make sure you wear gloves and Mask(N95 is better).
STEP 7
Clean All
For FDM 3D Printer you are ready to go.
For SLA 3D Printer you still need to use UV lamp to cure your model and clean it.